Managing CPU load when using Echo
- Live Versions: All
- Operating System: All
Echo is designed to be as CPU-efficient as possible, however there are certain features which can tax the CPU more heavily than others. If you encounter high CPU load or dropouts while using Echo, try minimizing the usage of the features below.
Note: You can find more information in our Learn Live 11: Computer Performance video tutorial to help reduce the CPU load.
General
- CPU resources are freed up whenever a device is silent. If a device is not passing any signal, then Live will "silence" it so that no CPU resources are wasted. It can take some time until Echo turns into its energy saving state because Live has to measure that all parameters, such as its reverb, are really silent (see also Reverb).
- Because of the nature of the device, it is easy to end up in a state where Echo is never really silent, thus impacting the CPU severely depending on the circumstances (how many instances, which kind of Live set).
- Using the "Gate" feature (under Character tab) is an effective way of preventing Echo from passing signals under a certain threshold, therefore improving overall CPU performance. (see also Gate).
Feedback
A high feedback amount can cause the device to infinitely repeat the signal, and that takes a toll on the CPU even if the device itself is not being heard (e.g. channel is muted/faded out).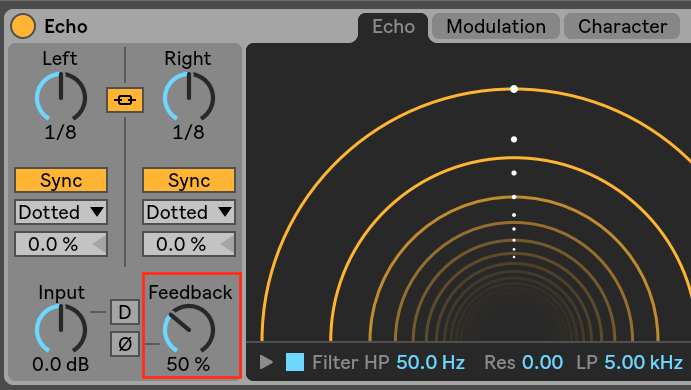
Delay Time
Different delay times, free or synced, should not impact the CPU in a significant way. However, the longer the delay time, depending on the amount of signal, will keep the device in an "active" state: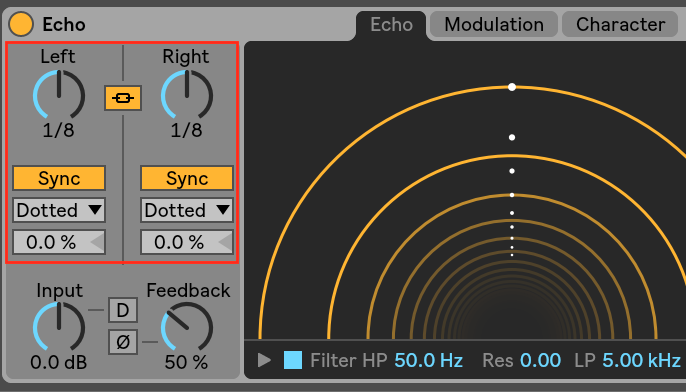
Reverb
Echo uses a classic plate reverb per channel. Hence the reverb effect is quite CPU heavy. To lower the the CPU usage, set the Reverb amount to 0%: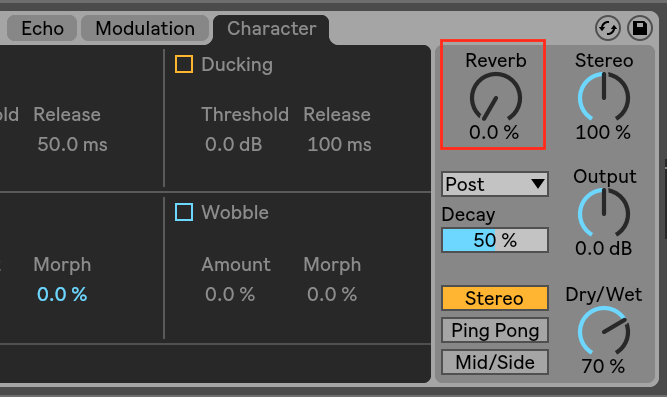
Filter
Echo uses the Cytomic PRD filter which is CPU demanding. Disabling the filter reduces Echo's CPU load significantly: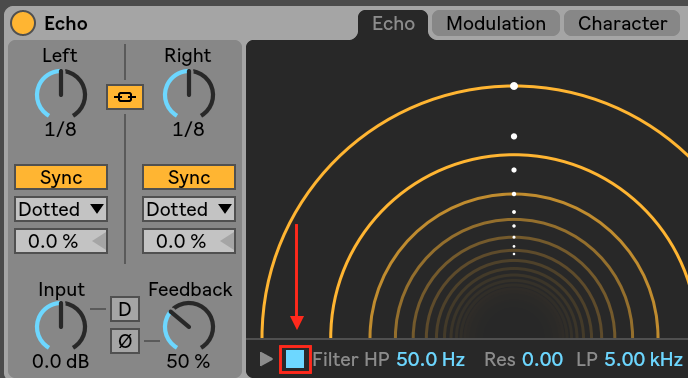
Gate
This parameter improves performance depending on its setting, in that it silences the device input whenever that is below a certain threshold (see also Delay Time).
Noise
Using Noise from Echo's Character section has the potential of increasing CPU usage, due to the fact that the device will never be completely silent and never turn into its energy saving state. Therefore, it's almost always a good idea to combine the noise with the gate:
Windows
On Windows, make sure that “High Performance” is active in the Windows Power Plan. See this third party guide to setting a high performance power plan on Windows.